Pure substances are defined as substances that are made of only one type of atom or only one type of molecule (a group of atoms bonded together). For example, pure iron would only contain iron atoms.
3.2 PHASE OF A PURE SUBSTANCE
Substances exist in different phase under different conditions. Even though there are 3 principal phases-solid, liquid, and gas, a substance may have several phases within a principal phase, each with a different molecular structure.
- In solids, the molecules are kept at their positions by the intermolecular forces.
- In liquids, the intermolecular forces are weak and the molecules are no longer at fixed positions, they can rotate and translate freely.
- In gas, the intermolecular forces are very small and the molecules are far apart from each other and move randomly.
3.3 PHASE CHANGE PROCESSES OF PURE SUBSTANCES


Saturation Temperature - the temperature at which a pure substance changes phase at a given pressure
Saturation Pressure - the pressure at which a pure substance changes phase at a given temperature
* Water boils at 100 Celcius at 1 atm pressure.
Latent heat - the amount of energy absorbed or released during a phase-change process
Latent heat of fusion - the amount of energy absorbed during melting / the energy released during freezing
Latent heat of vaporization - the amount of energy absorbed during vaporization / the energy released during condensation
* A substance at higher pressures boils at higher temperatures.
 |
| From the diagram, Tsat increases with Psat. |
3.4 PROPERTY DIAGRAMS FOR PHASE-CHANGE PROCESSES
* T-V Diagram


* P-T Diagram

* P-V-T Surface
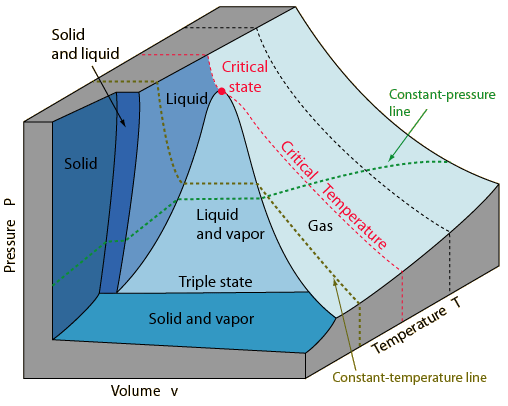 |
| P-V-T surface of a substance that contracts on freezing |
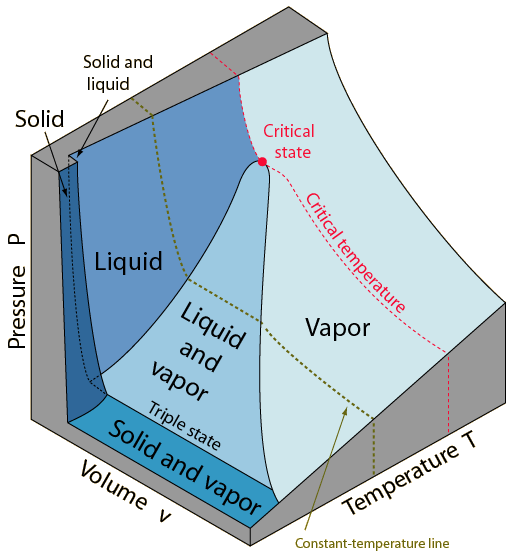 |
| P-V-T surface of a substance that expands on freezing |


No comments:
Post a Comment