
 |
| Mechanisms of Energy Transfer |
2.2 Forms of Energy

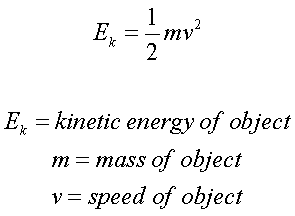
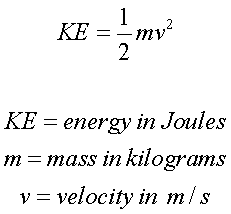


Mass flow rate is the amount of mass flowing through a cross section per unit time.
m = pV (kg/s) where p is the fluid density and V is the volume of fluid.
Energy flow rate associated with a fluid flowing at a mass flow rate.
E = me (kJ/s or kW)
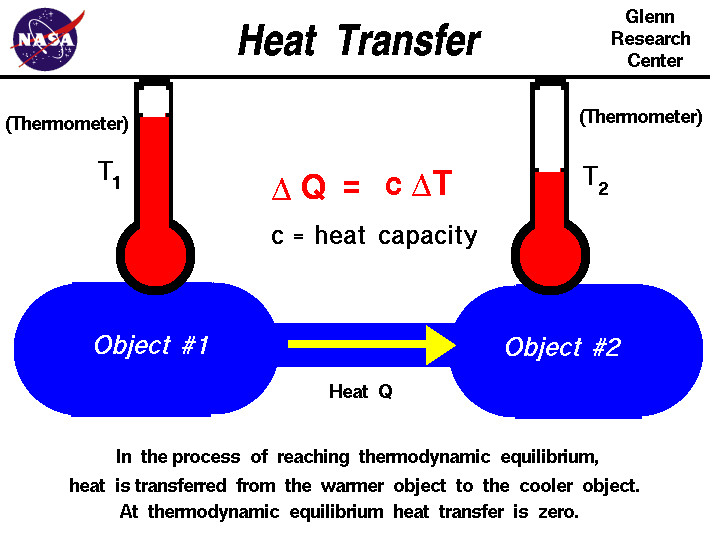
2.3 ENERGY TRANSFER BY HEAT
Heat is defined as the form of energy that is transferred between two systems (or a system and its or surroundings) by virtue of a temperature difference. The rate of heat transfer is high when the temperature difference is large.
A process during which there is no heat transfer is called an adiabatic process. The process is only adiabatic either when the system is well insulated so that only a negligible amount of heat can pass through the boundary, or both the system and the surroundings are at the same temperature and therefore there is no driving force (temperature difference) for heat transfer.
No comments:
Post a Comment