1.1 Thermodynamics and Energy
Thermo dynamics
(Heat) (Power)
Thermodynamics is the study of the effects of work, heat and energy on a system.
Thermodynamics Laws >>>>>>
- 0th Law - Thermal equilibrium

- 1st Law - Conservation of energy,energy cannot be destroyed but can change forms

- 2nd Law - Energy has quantity and direction, entropy

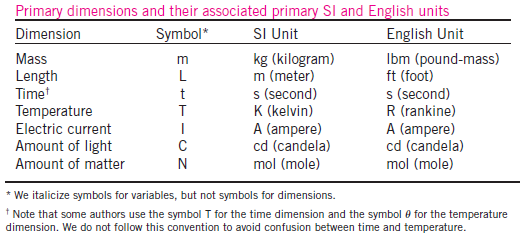
1.2 Importance of Dimensions and Units
1.3 Systems and Control Volume




System
|
Closed System
(Control mass)
|
Open System
(Control volume)
|
Heat and
Work
|
Heat and work (energy) crosses the
system when undergoing a process
|
Heat and work (energy) crosses the
system when undergoing a process
|
Mass
Transfer
|
Without any mass transfer when
undergoing a process
|
With mass transfer when undergoing a
process
|
Example
|
Closed piston cylinder, bomb
calorimeter, pressure cooker
|
Turbine, compressor, nozzle
|
1.4 Properties of a System
- Intensive properties (Independent on mass) - Pressure P, Temperature T, Density ρ
- Extensive properties (Dependent on mass) - Mass m, Volume V
Density = mass per unit volume
Specific volume = volume per unit mass
v = V/m = 1/ρ
Specific gravity = density of substance / density of water
1.6 State and Equilibrium
- Thermal Equilibrium - temperature constant throughout the system
- Mechanical Equilibrium - constant pressure at any point of the system with time
- Phase Equilibrium - two phases where the mass of each phase reaches an equilibrium level and stays there
- Chemical Equilibrium - the chemical composition of a system dos not change with time
The State Postulate
- Simple compressible system is a system in the absence of external forces including electrical, magnetic, gravitational, motion and surface tension effects.
- State Postulate states that the state of a simple compressible system is specified by two independent intensive properties, which are temperature and pressure for single phase system.
No comments:
Post a Comment